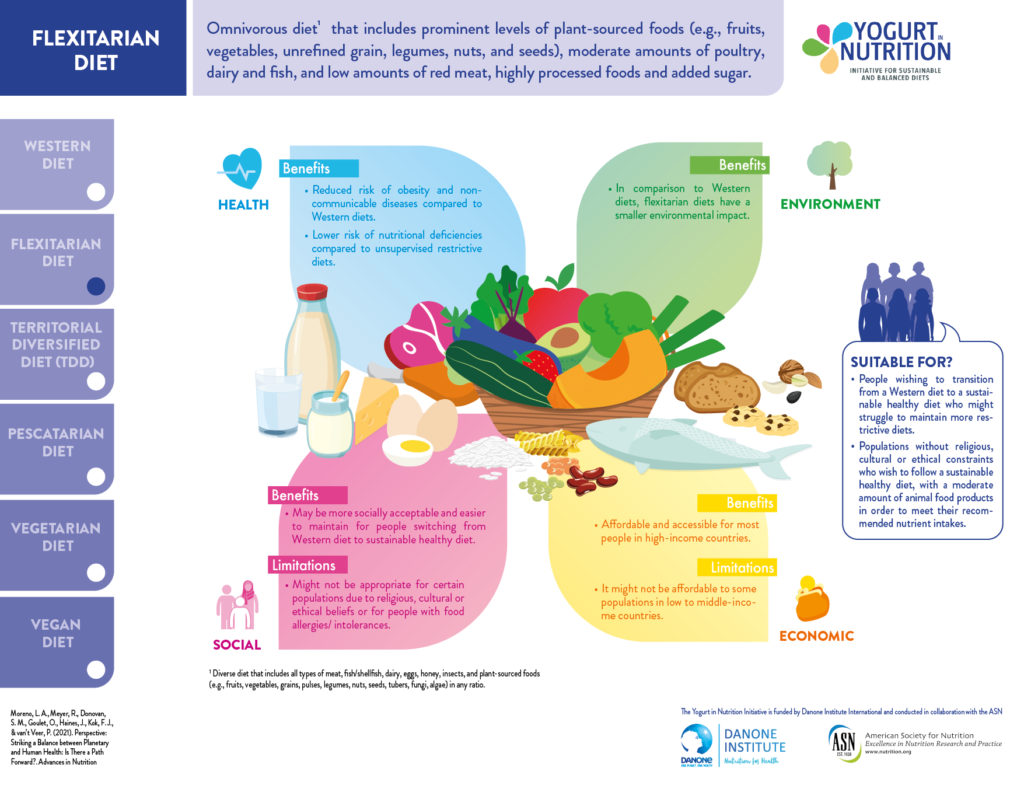
Flexitarism or Flexitarian diets are generally plant-rich diets with fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds, which include modest amounts of animal-based products such as eggs, dairy products, meat and fish [1].
It differs from vegetarian or vegan diets, as it is more flexible and still allows to eat meat.
How to eat a flexitarian diet?
There are no specific rules for a “good flexitarian diet” but the main approach is to:
- Promote the consumption plant-based foods such as of fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds and wholegrains.
- Limit the consumption of ultra-processed foods.
- Limit the consumption of sugar and sweets (soda, candy, pastry…).
- Consume meat and animal-sourced foods occasionally. In details, the flexitarian dietary patterns contain the least amount of processed meat, small amounts of red meat, including beef, lamb, and pork (one serving per week) and moderate amounts of poultry, egg, and fish. [2]
Flexitarian diet and environment
The flexitarian diet can be considered as a way to build a sustainable diet: As it reduces the part of animal-sourced foods consumption, it helps to decrease the greenhouse gas emissions, as well as land and water use and has a lower impact on the environment. However, the occasional consumption of animal-sourced foods assures the nutritional needs and limits the risk of nutrient deficiency (such as vitamin B12 and required iron amount). Flexitarian diets is an interesting compromise for a more balanced and sustainable diet. [3]
Flexitarian diet and health
In addition, the healthy mix of nutrients in flexitarian diets, including high-quality protein, fiber, vitamins, mineral and healthy fatty acids, may provide several health benefits. Studies suggest that flexitarian is beneficial for weight control and metabolic health benefits (reduced risk of type 2 diabetes and blood pressure) compared with the typical non-vegetarian diet [3].
Conducting studies on the flexitarian diet, the WorldWide Fund for Nature (WWF) concluded that flexitarian diets offer a balance that allows families to:
- Eat more healthily
- Eat quality products while protecting the environment
- Cut the carbon footprint from their food
- Reduce pressure on land and marine resources. [4]
For more information, discover:
- our detailed evidence-based document about flexitarian diet
- the detailed infographic about the differents diets and their impacts on health and environment