This Digest is all about #Yogurt and #WeightManagement
Overweight and obesity are vital, global, public health issues. According to the World Health Organization, obesity has more than doubled worldwide since 1980, and in 2014, 39% of adults were overweight and 13% were obese (Figures 1 and 2) (1).

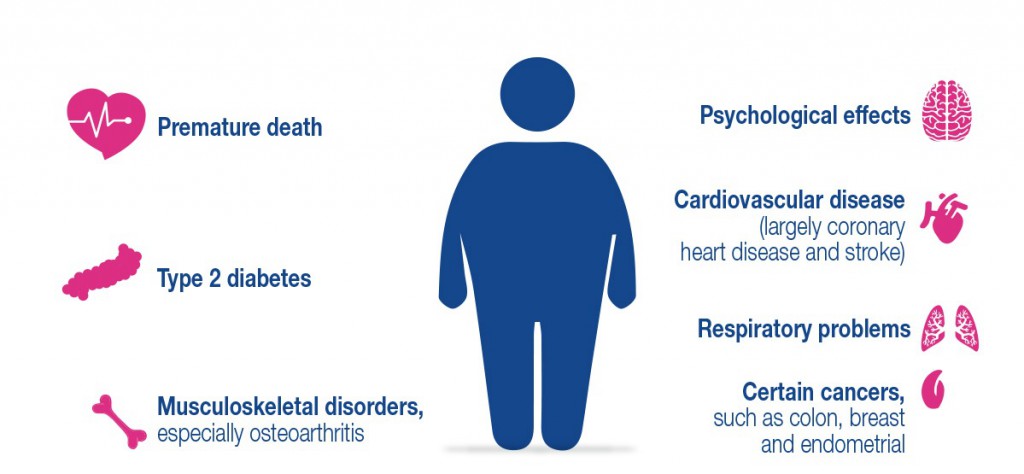
Obesity not only has serious implications for individuals’ health and well-being (see Figure 3), but for health services and the wider economy. So, why do we have an obesity crisis? Is a simple case of us eating more and moving less?
Changes in eating habits and physical activity patterns, as a result of wider environmental and societal changes have been proposed as key factors behind the obesity epidemic. We appear to be eating more foods that are lower in nutrients and higher in energy density, our portion sizes have grown, and we’re increasingly eating outside the home – which often means exposure to higher calorie foods (2, 3). The displacement of nutrient rich foods and drinks with nutrient-poor items may be influencing childhood obesity, which in turn impacts adulthood obesity (4-6). Add to this the fact that we’re working in a more sedentary capacity and we begin to see a pattern of association between the rise in obesity and lifestyle changes.
Obesity is complex, but in our food-filled environment, any eating pattern that can give weight management a helping hand could be beneficial for people of all ages. For example, eating more yogurt, nuts, fruit, whole grains or vegetables was associated with gaining less weight over a 4 year period amongst 120,000 adults, followed up for more than 16 years – with the association being strongest for yogurt (0.82lb less weight gain for each additional serving per day) (7).
References:
- WHO facts http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/.
- Kant AK. Consumption of energy-dense, nutrient-poor foods by adult Americans: nutritional and health implications. The third National Helath and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988-1994. Am J Clin Nutr 2000; 72(4):929-36.
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evalution, Global burden of disease 2013. http://www.healthdata.org/infographic/obesity-and-overweight-increasing-worldwide.
- Frary CD et al. Children and adolescents’ choices of foods and beverages high in added sugars are associated with intakes of key nutrients and food groups. Journal of Adolescent Health 2004; 34(1):56–63
- Ballew C et al. Nutrient intakes and dietary patterns of young children by dietary fat intakes. J Pediatr 2000; 136:181–187.
- Bowman SA, et al. Effects of fast-food consumption on energy intake and diet quality among children in a national household survey. Pediatrics 2004; 113:112-132.
- Mozaffarian D, Hao T, Rimm EB, Willett WC, Hu FB. Changes in diet and lifestyle and long-term weight gain in women and men. NEJM 2011; 364(25):2392-404.
Can yogurt reduce your chances of being overweight?
There is a wide-ranging body of scientific evidence suggesting a beneficial relationship between a regular intake of dairy foods and weight, as well as body fat (8, 9). A systematic review of 22 studies suggested that yogurt consumption is associated with lower Body Mass Index (BMI), lower body weight and weight gain, smaller waist circumference and lower body fat (10).
Six cross-sectional studies have examined the relationship between yogurt and BMI. Five found a beneficial association (yogurt consumers had a significantly lower BMI than non-consumers) in females only for two of these studies (11, 12), and in both genders for three studies (13-15), while one showed no effect of yogurt on BMI (16).
In addition, in one of these studies (13), it was found that people who ate more than three servings of yogurt a week gained about 55% less weight over a year compared to those who ate less than one serving per week. When it came to waist size, higher yogurt consumers gained 20% less than lower yogurt consumers.
A Mediterranean cohort study found that high yogurt consumption (seven or more servings per week) at baseline was associated with a 20% lower risk of overweight or obesity after 6 years. This inverse association was stronger if consumption was coupled with high fruit intake (32% risk reduction) (17).
The CARDIA study (a prospective cohort study amongst a large group of young adults) showed that total dairy intake significantly reduced the risk of overweight people becoming obese. However, there was no significant association between yogurt intake per se (18).
References:
8. Jacques PF, Wang H. Yogurt and weight management. Am J Clin Nutr 2014; 99(5 Suppl):1229S-34S. http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/99/5/1229S.full.pdf.
9. Astrup A, Chaput JP, Gilbert JA, Lorenzen JK. Dairy beverages and energy balance. Physiol Behav 2010; 100(1):67-75.
10. Eales J, Lenoir-Wijnkoop I, King S, Wood H, Kok FJ, Shamir R, Prentice A, Edwards M, Glanville J, Atkinson RL. Is consuming yoghurt associated with weight management outcomes? Results from a systematic review. International Journal of Obesity, advance online publication nov 2015. http://www.nature.com/ijo/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/ijo2015202a.html
11. Gugger C, Joshi N, Albertson A. Yogurt consumption is associated with lower body weight status and improved nutrient intakes in adult women. FASEB Journal 2014; 1.
12. Joshi NA, Albertson AM, Bell E. Yogurt intake is associated with favorable nutrient intake and healthy body measures in US women: Results from NHANES 2007-08. FASEB Journal 2011; 25.
13. Wang H, Troy LM, Rogers GT, Fox CS, McKeown NM, Meigs JB, Jacques PF. Longitudinal association between dairy consumption and changes of body weight and waist circumference: the Framingham Heart Study. Int J Obes 2014; 38(2):299-305.
14. Beydoun MA, Gary TL, Caballero BH, Lawrence RS, Cheskin LJ, Wang Y. Ethnic differences in dairy and related nutrient consumption among US adults and their association with obesity, central obesity, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 87(6):1914-25.
15. Wang H, Livingston KA, Fox CS, Meigs JB, Jacques PF. Yogurt consumption is associated with better diet quality and metabolic profile in American men and women. Nutr Res 2013; 33(1):18-26.
16. Murphy KJ, Crichton GE, Dyer KA, Coates AM, Pettman TL, Milte C, et al. Dairy foods and dairy protein consumption is inversely related to markers of adiposity in obese men and women. Nutrients 2013; 5(11):4665-84.
17. Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Sayon-Orea C, Ruiz-Canela M, de la Fuente C, Gea A, Bes-Rastrollo M. Yogurt consumption, weight change and risk of overweight/obesity: The SUN cohort study. Nutrition, metabolism, and cardiovascular diseases. NMCD 2014; 24(11):1189–1196.
18. Pereira MA, Jacobs DR, Jr., Van Horn L, Slattery ML, Kartashov AI, Ludwig DS. Dairy consumption, obesity, and the insulin resistance syndrome in young adults: the CARDIA Study. JAMA 2002; 287(16):2081-9.
Can yogurt give you curves in the right places?
A large Spanish cohort study found that whole fat yogurt consumption (7 or more servings per week) was associated with a 15% reduced risk of developing central adiposity (waist circumference ≥102 cm in males and ≥88 cm in females) (19).
Two other cohort studies provide evidence for a negative association between yogurt consumption and waist circumference in overweight people over a follow-up period of 6 or 12.9 years (13, 20).
A significant negative association between yogurt consumption and waist circumference for both sexes has also been reported by three cross-sectional studies (14, 16, 21). And, in a study of Canadian adults, yogurt consumption was associated with lower body weight, waist to hip ratio, waist circumference and tended to be associated with a lower BMI (22).
References:
19. Sayon-Orea C, Bes-Rastrollo M, Martí A, Pimenta AM, Martín-Calvo N, Martínez-González MA. Association between yogurt consumption and the risk of Metabolic Syndrome over 6 years in the SUN study. BMC Public Health 2015; 15:1518.
20. Vergnaud AC, Peneau S, Chat-Yung S, Kesse E, Czernichow S, Galan P, et al. Dairy consumption and 6-y changes in body weight and waist circumference in middle-aged French adults. Am J Clin Nutr 2008; 88(5):1248-55.
21. Albertson AM, Holschuh NM, Eldridge AL. Yogurt consumption in the United States: Effect on nutrient intakes and body measures in adults 19+ years. FASEB Journal 2007; 21(6):A1061.
22. Cormier H. Thifault E, Garneau V, Tremblay A, Drapeau V, Pérusse L, Vohl MC. Association between yogurt consumption, dietary patterns, and cardio-metabolic risk factors. Eur J Nutr 2015; Mar 15.
Yogurt consumption and weight and fat loss
There is only a very small amount of evidence relating to yogurt consumption and weight and fat loss.
A randomised controlled trial (RCT) by Zemel and colleagues (23) indicated that when yogurt is part of an energy-restricted diet for overweight/obese people, yogurt supplementation can help to significantly reduce body weight compared to a placebo control (sugar-free gelatine dessert) over 12 weeks. However, two other RCTs found no weight loss differences between yogurt and control groups (24, 25).
References:
23. Zemel MB, Richards J, Mathis S, Milstead A, Gebhardt L, Silva E. Dairy augmentation of total and central fat loss in obese subjects. Int J Obes 2005; 29(4):391-7.
24. Shlisky JD, Durward CM, Zack MK, Campbell JK, Jonnalagadda SS, Gugger C, et al. Effects of an energy-restricted, moderate-protein diet plan with non-fat dairy on weight changes: 12 weeks of weight loss (WL) followed by 12 weeks of WL maintenance. FASEB Journal 2012; 26.
25. Thomas DT, Wideman L, Lovelady CA. Effects of a dairy supplement and resistance training on lean mass and insulin-like growth factor in women. International Journal of Sport Nutrition & Exercise Metabolism 2011; 21(3):181-8.
Three Yogurt Weight Management Facts
There are a number of theories about how yogurt may effect body fat and give a helping hand to weight management:
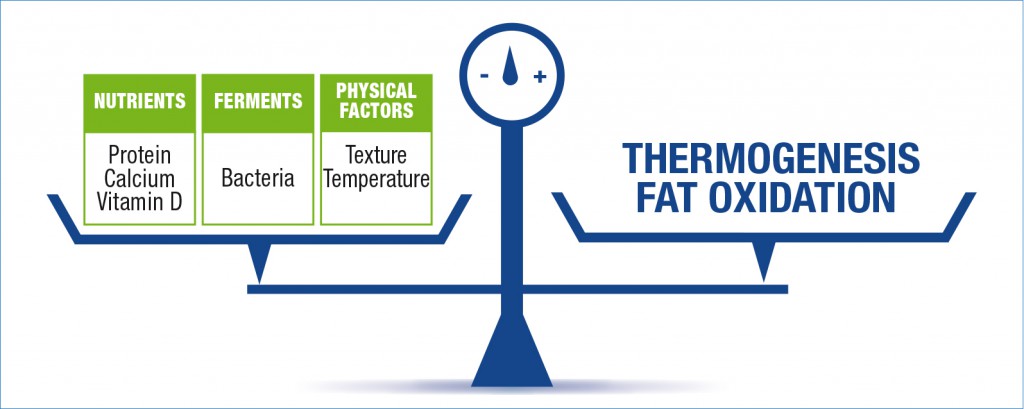
1. Yogurt is a good source of calcium and protein, containing more than an equivalent volume of milk. Several studies have shown that dietary calcium can bind fat and decrease its absorption from the intestinal tract (26). Calcium and dietary proteins such as whey and casein proteins, peptides and amino acids such as leucine may facilitate loss of weight and fat mass. For example, adequate calcium intake decreases levels of calcitriol, a calcium-regulating hormone, leading to decreases in intracellular calcium and less fat being stored in adipocytes which may result in weight loss (27, 28).
2. Yogurt as a fermented food that can contain live and active cultures may be able to change colonic bacteria that might influence weight gain (8, 29).
3. Yogurt, especially protein-rich yogurt, has a potential role in promoting satiety. Studies suggest that protein enhances satiety and satiation and can lead to a reduction in appetite (Digest 2).
It is also possible that people who increase or decrease their yogurt consumption may have other linked weight-influencing behaviours that have not as yet been measured or identified in reported studies (7).
References:
26. Christensen R, Lorenzen JK, Svith CR, Bartels EM, Melanson EL, Saris WH, Tremblay A, Astrup A. Effect of calcium from dairy and dietary supplements on faecal fat excretion: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev 2009; 10(4):475-86.
27. Zemel MB. Role of calcium and dairy products in energy partitioning and weight management. Am J Clin Nutr 2004; 79: 907S–912S0.
28. Zemel MB. The role of dairy foods in weight management. J Am Coll Nutr 2005; 24:537S–46S.
29. Kallus SJ, Brandt LJ. The intestinal microbiota and obesity. J Clin Gastroenterol 2012; 46:16–24.
Science to spoon
A successful weight management plan can be built around a range of healthy foods, incorporating a realistic physical activity plan, behaviour-change techniques and support. Ideally, a programme should be managed within a multi-disciplinary team of experts with an aim to achieve and keep to a healthy weight as part of a long-term lifestyle change.
At the end of this Digest, you’ll see a hand-out for your patients and clients: examples of mindful eating techniques, healthy eating tips and menu suggestions for incorporating dairy foods (including yogurt) into a balanced meal plan.
Eating for a healthy weight needn’t be about counting calories; check out these practical hints and tips to help you enjoy a wide range of tasty foods, including yogurt, whilst keeping a watchful eye on your weight.
Five foodie tips
1. Eat regular meals, especially breakfast. Missing meals can make you give in to temptation and you
might reach for unhealthy snacks that don’t offer you nutrients or a feeling of fullness.
2. Fill up on fibre. Fruit and vegetables are typically low in calories, high in fibre and low in fat – they also provide essential nutrients for health, and are low in energy density (calories per bite!). Aim for at least five servings of fruit and veg a day. High fibre foods help promote satiety – whole grains like oats, brown rice, pasta and bulgur wheat; and vegetables such as beans and pulses.
3. Cut down on unwanted fat, for example by avoiding fried foods, choosing lean cuts of meat and lower fat cooking methods like grilling and steaming. As a general rule, choose high protein lower fat dairy foods to help fill you up and provide essential nutrients including calcium and phosphorus. Lower fat dairy foods still have the same amount of calcium as full fat varieties. Aim for 3 servings of lower fat dairy a day (3-4 dairy servings seem to be the usual amount used in RCTs) (Figure 6).
4. Keep to within the recommended alcohol limits and ideally have no more than one unit of alcohol a day to keep your calorie intake down.
5. Watch portion sizes – using a smaller plate and checking recommended portion sizes on packaged foods helps.
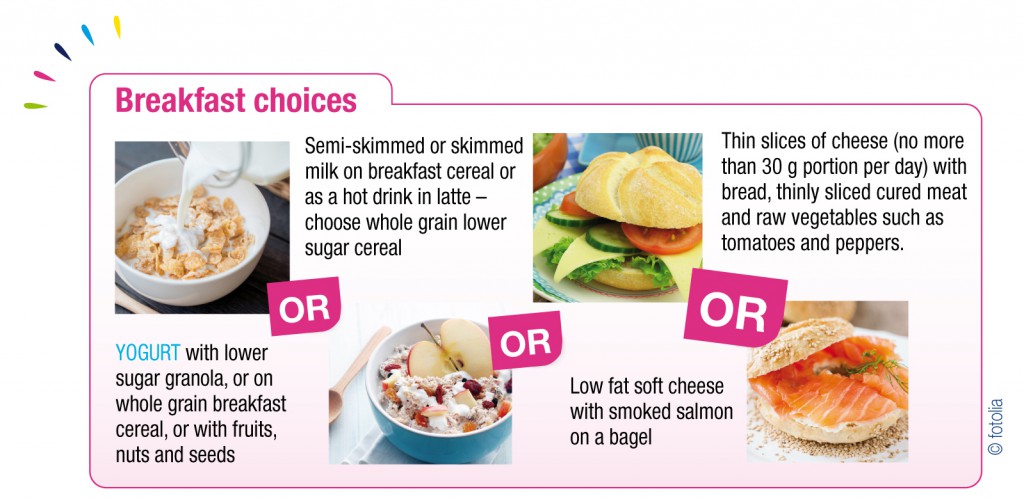
Menu ideas for breakfast
Eating for a healthy weight needn’t be about counting calories; check out these practical hints and tips to help you enjoy a wide range of tasty foods, including yogurt, whilst keeping a watchful eye on your weight.
Menu ideas for lunch
Eating for a healthy weight needn’t be about counting calories; check out these practical hints and tips to help you enjoy a wide range of tasty foods, including yogurt, whilst keeping a watchful eye on your weight.
Menu ideas for in between meals
Eating for a healthy weight needn’t be about counting calories; check out these practical hints and tips to help you enjoy a wide range of tasty foods, including yogurt, whilst keeping a watchful eye on your weight.
Menu ideas for dinner
Eating for a healthy weight needn’t be about counting calories; check out these practical hints and tips to help you enjoy a wide range of tasty foods, including yogurt, whilst keeping a watchful eye on your weight.
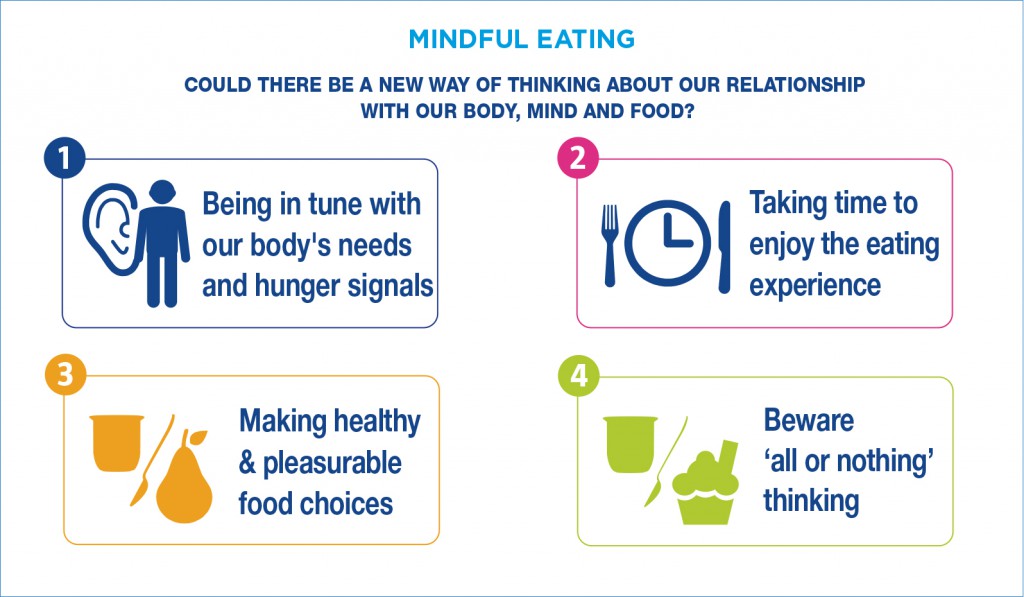
Eating Mindfully
Your mind-set can make or break your healthy weight goals. We eat for many different reasons, for example, in response to emotions, the sight of food, social situations, boredom, habit and hunger. Here are some suggestions that could help you get your brain in gear.
- Make conscious choices
Always try to stop, think, and make a conscious choice before you eat. Really choosing whether you eat something, or not, not only keeps you focused but can stop you feeling deprived. Keeping a food diary can help you to make conscious choices, as you’re more aware of what you’re eating and when.
- Follow an eating plan
See the menu on Figure 5 as an example of a structured menu plan.
Decide on the times that you will have each meal, and when you will eat 2-3 wise, planned snacks, such as fruit, yogurt, handful of nuts, over the day. If you think you feel hungry, drink some water, and try to wait until the next planned time to eat, and distract yourself by doing something else. This is a good way to tell the difference between real hunger and other triggers for eating. You will often find that the urge to eat has passed.
- Choose satisfying foods
Foods that have a low energy density (foods that are lower in calories compared to other foods of the same weight) may help you to feel fuller for longer and, in turn, help you eat more mindfully and stay on track. These tend to be foods that give you protein and/or bulky fibre, for example, yogurt, fruit, vegetables, pulses, seafood and soup. Further, emerging research seems to suggest that full fat dairy products may be beneficial in weight management (30).
- Beware ‘all or nothing’ thinking
If you can’t fend off a craving or snack attack, you haven’t ‘failed’ or ‘ruined everything’. Instead, see it as a learning experience. Plan how you might deal with it differently next time, forgive yourself and move on. Don’t let lapses push you off course. Ups and downs like these are normal. Enlisting support from a friend, partner, healthcare professional, group or on-line community can help too.