“Yogurt can enhance satiety and help to manage energy intake” is one of the 10 evidence-based conclusions made by the YINI board about the health effects of yogurt. Learn more below…
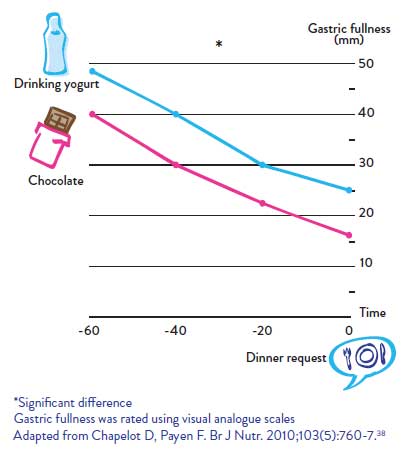
Yogurt achieves greater satiety than high energy-dense snack foods such as chocolate
Among healthy young men, a yogurt drink taken as a mid-afternoon snack induced a greater feeling of fullness in the hour before a meal than a chocolate bar of the same calorie content.
High-protein yogurt could be a healthy replacement for high energy-dense snacks
Consuming yogurt as a high-protein, less energydense
snacks instead of high-fat snack foods can improve appetite control and satiety, and reduce energy intake.
- Women participating in a study were less hungry after consuming a mid-afternoon snack of highprotein yogurt than after consuming high-fat crackers or chocolate.
- Despite having the same calorie content as the high-fat snacks, yogurt delayed the participants’ desire to eat the next meal by around 30 minutes.
- Moreover, the women consumed around 100 fewer calories after consuming yogurt than after eating crackers or chocolate.
References:
- Chapelot D, Payen F. Comparison of the effects of a liquid yogurt and chocolate bars on satiety: a multidimensional approach. Br J Nutr 2010;103:760–7.
- Ortinau LC, Hoertel HA, Douglas SM, et al. Effects of high-protein vs. high-fat snacks on appetite control, satiety, and eating initiation in healthy women. Nutr J 2014 ;13:97.



