The gut microbiota is a hot topic for everyone! We all carry trillions of bacteria within our gut and these microbial companions do all kind of things for us. They help maintain our gut health, they help our immune system to develop, and they also very probably have a role over certain diseases, like type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Inappropriate dietary habits or excessive use of antibiotics are examples of elements that may lead to a disturbance in the gut microbiota composition. One possible disturbance of the gut microbiota is known as dysbiosis. Dysbiosis is observed in individuals with some chronic diseases such as metabolic syndrome, obesity, allergies and type 2 diabetes.
“Non-communicable diseases like type 2 #diabetes, #obesity, heart diseases represent a major #publichealth concern worldwide #yogurt2017”
A balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle can contribute to correct or prevent dysbiosis.
On a day-to-day basis, what we eat is without a doubt interacting with our microbial friends. So there is a great interest to explore how our diet habits can help us to positively impact our health and prevent dysbiosis.
A lot of research is currently exploring dietary options that may be valuable for a healthy gut microbiota. In this respect, the consumption of probiotics, which are live microbes that we consume and that confer a health benefit on the host, as well as prebiotics, which are food ingredients that favor the growth of beneficial microorganisms, draw a lot of attention. In this context, fermented foods, when they are a source of live ferments, such as yogurt, seem to offer a relevant dietary solution.
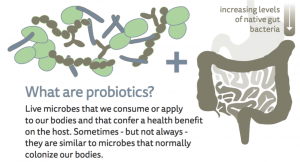
“Taking care of the #gut #microbiota through #diet appears to be an obvious strategy to preserve our health status #yogurt2017”
Fermented foods thus represent a particular nutritional interest.
On the one hand, the fermentation process, namely the transformation by microbes of foods into other foods, brings added value: enhanced safety, shelf-life and nutrition value. On the other hand, fermented foods such as yogurt can also contain live ferments, which can confer health benefits, once they are delivered into the gastrointestinal tract.
“Consumption of #probiotics & fermented foods is studied as a means to positively impact the #gut #microbiota #yogurt2017”

Key messages
- There is growing evidence on the link between dysbiosis – a microbial imbalance in the gut microbiota – and certain pathologies. The World Health Organization identifies four main types of non-communicable diseases (cardiovascular diseases like heart attacks and stroke, cancers, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes). These non-communicable disseases represent a major public health concern worldwide.
- Taking care of the gut microbiota through diet appears to be an obvious strategy to preserve our health status.
- In this perspective, the consumption of probiotics and fermented foods is studied as a means to positively impact the gut microbiota and therefore prevent dysbiosis or any other dysfunction.
Read further about the gut microbiota, dysbiosis, probiotic and fermented foods:
-
A report on Prof Sharon Donovan’s talk about the possible benefits of yogurt on the gut microbiota, which she presented during the EB 2016 in San Diego
-
A recap article about gut microbiota dysbiosis with an infographic
-
An infographic by the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics on the gut microbiota, our microbial partners
-
An infographic by the International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics on the effects of probiotics and prebiotics on our microbiota
-
A TED talk by Prof Rob Knight entitled “how our microbes make us who we are”



