This Digest is all about #Yogurt, #Protein & #AppetiteControl
Satiety and satiation signallers
Satiety is the feeling of satisfaction we get after we have eaten a meal and has an important influence on how much we eat overall. If satiety lasts for a while, it can reduce how much food we eat at the next meal or snack. Alongside satiety is ‘satiation’ – the process leading an individual to stop eating (1).
 Figure 1: Appetite control
Figure 1: Appetite control
Satiety & satiation signalers
As food is eaten, digested, absorbed and then metabolised, it triggers an orchestra of satiety influencing hormones, peptides and nerve messages from the gut, the brain and the body’s fat cells (1). As well as these physiological responses, satiety & satiation are influenced by many factors including our food beliefs, emotions, the taste and smell of food, and our immediate environment (1) – we can always manage that tempting dessert from a buffet table, or comforting crisps or chocolate, no matter how full we feel! Foods that give satiation signals a helping hand could benefit people to manage their health and weight in our food-filled environment. As evidence supports energy (calories) from protein being more satiating than energy from carbohydrate or fat (1, 2), the effect of protein-rich foods on appetite control is a hot topic.
References:
1. Benelam B. Satiation, satiety and their effects on eating behaviour. Nutr Bull.; 2009, 34, 126-173.
2. Paddon-Jones D, Westman, Mattes RD et al. Protein, weight management, and satiety. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(5):1558S-1561S.
Protein, the highest satiating macronutrient
A protein-rich meal or meal preload increases satiety & satiation
When researchers want to test the effect of protein on fullness, they often use a preload design, where the test food is eaten before a meal. A literature review reported that in the majority of studies, a protein preload significantly enhanced satiety ratings – in other words, appetite was reduced (3). Studies suggest that protein leads to a reduction in appetite[/mks_pullquote] Taking this a step further, researchers have found that compared to a typical protein breakfast (10% energy from protein), a higher protein breakfast (25% energy from protein) led to a more pronounced reduction in appetite (but no reduction in energy intake at the next meal). A more pronounced increase in appetite-regulating hormones was observed after the high protein meal (4, 5, 6).
References:
3. Halton, T.L., and F.B. Hu. The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004; 23: 373-385.
4. Veldhorst M, Nieuwenhuizen AG, Hochstenbach-Waelen A, et al. Comparison of the effects of a high- and normal-casein breakfast on satiety, ‘satiety’ hormones, plasma amino acids and subsequent energy intake. Br. J. Nutr. 2009; 101: 295-303.
5. Veldhorst M, Nieuwenhuizen AG, Hochstenbach-Waelen A, et al. Effects of high and normal soy protein breakfasts on satiety and subsequent energy intake, including amino acid and ‘satiety’ hormone responses. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009; 48: 92-100.
6. Veldhorst MA, Nieuwenhuizen AG, Hochstenbach-Waelen A, et al, Effects of complete whey-protein breakfasts versus whey without GMP-breakfasts on energy intake and satiety. Appetite, 2009; 52: 388-95.
Dairy and yogurt protein favour satiety
Dairy and yogurt protein favour satiety and help you eat fewer calories at the next meal
While the overall body of research to date indicates no clear view that one type of protein can help us feel fuller for longer than another (7), there remains a strong interest in the potential benefit of whey protein. Whey and casein protein are the key dairy proteins, and whey protein is more rapidly digested and absorbed (8).
Lorenzen et al (9) found that milk was more satiating than whey or casein alone. This may be because of the unique combination of a ‘slow’ and a ‘fast’ protein found in milk. No significant difference on postprandial energy expenditure was observed. However, a small but significant increased lipid oxidation was observed after casein compared with whey.
Akhavan et al. (10) tested different combinations of water and whey protein in a meal preload to test its impact on people’s energy (calorie) intake at lunchtime. Interestingly, the protein containing preload resulted in a “negative calorie effect” – the size of the calorie reduction at the lunch was greater than the calories in the protein preload.
Keeping to a healthy weight isn’t easy, especially when constantly surrounded by tempting foods. There is no quick-fix. Lifestyle habits that allow us to enjoy a varied diet, regular eating patterns and physical activity are the key to long-term weight management. Recent studies (11) suggest that “sleeping well” is also a key issue in the prevention of excess body weight.
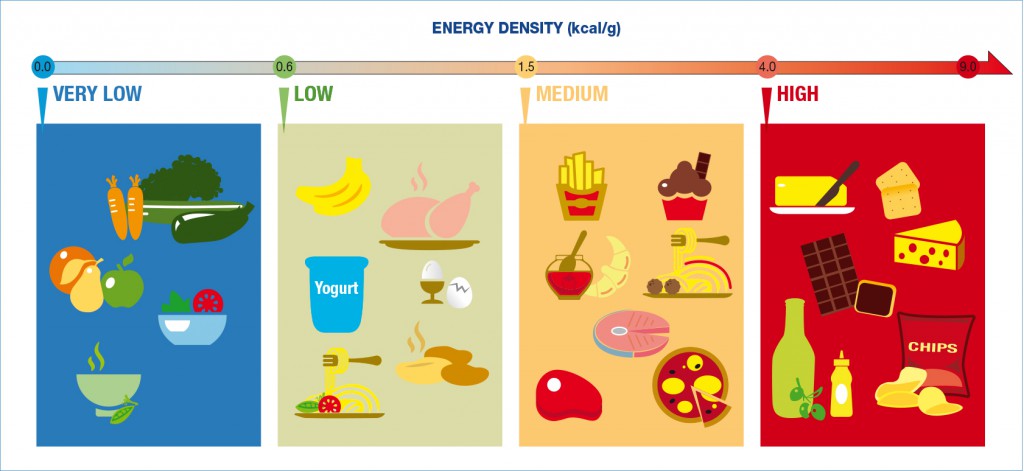
Anything that offers a helping hand is good news. Diets with a low energy density have been shown to help improve satiety (12). Energy density is defined as the number of calories/weight (in grams). Low energy dense foods provide between 0.6 to 1.5 kcal/g. Low energy dense foods tend to have a high water content – soups, stews, fruits, and vegetables, for example. Many lower fat and higher fibre foods also have fewer calories per gram. The British Nutrition Foundation Feed Yourself Fuller Chart (13) clearly depicts low fat yogurt as having an energy density of 0.78 (0.78 kcal/g), which is classed as “low”.
Figure 1: Energy Density of selected food adapted from the Feed Yourself Fuller Chart (13)
References:
7. Gilbert, J.A., N.T. Bendsen, A. Tremblay, et al. Effect of proteins from different sources on body composition. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. (2011); 21(suppl. 2): B16-31.
8.Veldhorst, M.A., A.G. Nieuwenhuizen, A. Hochstenbach-Waelen, et al. Dose-dependent satiating effect of whey relative to casein or soy. Physiol. Behav. (2009) 96: 675-682.
9. Lorenzen J, Frederikson R, Hoppe C et al. The effect of milk proteins on appetite regulation and diet-induced thermogenesis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012 May; 66 (5):622-7.
10. Akhavan T, Luhovyy BL, Brown PH, et al. Effect of premeal consumption of whey protein and its hydrolysate on food intake and postmeal glycemia and insulin responses in young adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010; 91: 966-75.
11. Chaput JP, Leblanc C, Pérusse Louis et al. Risk Factors for Adult Overweight and Obesity in the Quebec Family Study: Have We Been Barking Up the Wrong Tree? Obesity (2009) Epidemiology Article 1-7.
12. Rolls BJ, Bell EA, and Thorwart ML. Water incorporated into a food but not served with a food decreases energy intake in lean women. Am J Clin Nutr 1999;70:448–55.
13.British Nutrition Foundation Feed Yourslef Fuller Chart 2009 http://nutrition.org.uk/attachments/423_13209%20BNF%20feed%20Poster_PRINT_2.pdf
High protein snacks and satiety
There is building evidence that a higher protein snack may be beneficial, thanks to its potential effects on satiety, and energy intakes in the next meal. A formulation of yogurt enriched with whey protein might further improve the acute satiating effect of yogurt (Tremblay, et al, unpublished data). High protein snacks have been shown to influence subsequent eating[/mks_pullquote] A study by Douglas and colleagues (14) assessed whether an afternoon snack could influence appetite sensations as well as eating initiation at dinner. The investigators randomly provided women with a yogurt snack that varied in protein content (5, 14, or 24 grams) or with no snack. Regardless of protein content, snacking resulted in reduced hunger and increased fullness. Further, hunger was lower and fullness was higher following the consumption of the high-protein yogurt as compared to the low-protein version. Interestingly, consumption of the high-protein snack delayed the onset of eating at dinner as compared to no snacking. While there was no difference in the energy content consumed between the yogurt snacks and no snack throughout the test day, the delayed onset of eating suggests that satiety was higher and the motivation to eat was less following the high-protein snack.
Reference:
14. Douglas SM, Ortinau, LC, Hoertel HA, et al. Low, moderate, or high protein yogurt snacks on appetite control and subsequent eating in healthy women. Appetite, 2013; 60, 117-122.
Protein and dairy rich foods influence “hunger hormones”
So how might protein, including dairy protein, influence hunger and satiety? One way appears to be via its effect on different appetite-regulating hormones released by the intestine and the brain. For example, a high protein meal has been shown to increase the levels of PYY and GLP1 (15), which seem to work to reduce appetite by slowing stomach emptying and via direct communication with the brain’s appetite-regulation centre in the hypothalamus and brain stem (2,16). A recent study highlighted a potential effect of dairy protein where compared to a low dairy/calcium weight loss diet, a high dairy/calcium diet resulted in higher blood levels of PYY and greater feelings of satisfaction after a meal. However this did not translate into a difference in weight loss (17).Written by Angelo Tremblay, Chris Cifelli and Azmina Govindji
References:
2. Paddon-Jones D, Westman, Mattes RD et al. Protein, weight management, and satiety. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(5):1558S-1561S
15. Van der Klaauw A, Keogh JM, Henning E, et al. High protein intake stimulates postprandial GLP1 and PYY release. Obesity 2013; 21: 1602-7.
16. Journel M, Chaumontet C, Darcel N, et al. Brain responses to high-protein diets. Adv Nutr 2012; 3:322–9.
17. Jones KW, Eller LK, Parnell JA, et al. Effect of a dairy- and calcium-rich diet on weight loss and appetite during energy restriction in overweight and obese adults: a randomized trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013; 67: 371-6.
Protein-rich yogurt for greater fullness & less hunger: research bytes
- Dairy products eaten as mid-morning snacks reduced appetite and lunch intake compared with water:
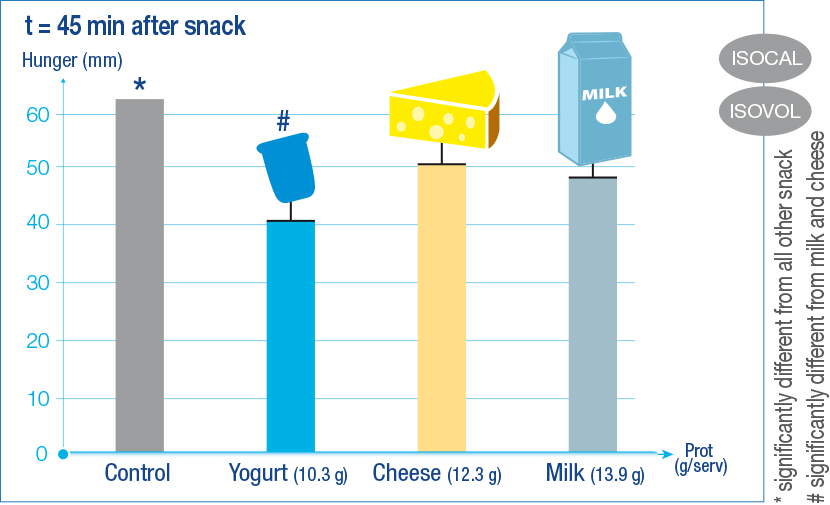
Yogurt reduced hunger ratings compared with servings of milk and cheese with the same calorie content and volume (18).
Figure 1: Hunger rating 45 min after dairy snacks, adapted from ref. 18
- A snack of protein-rich yogurt induces greater feelings of fullness compared to snacking on chocolate bar:
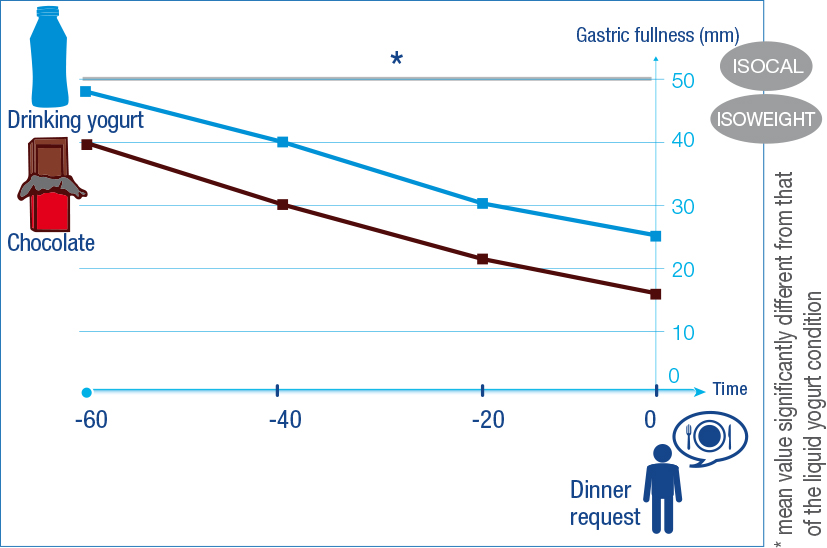
Young adults given an isocaloric afternoon snack of either a liquid yogurt or chocolate bar had higher satiety ratings (lower hunger, desire to eat, appetite and more feelings of fullness) for the hour before their evening meal after the liquid yogurt, which naturally contained 7.5g more protein (19).
Figure 2: Sensation of fullness after a drinking yogurt, or chocolate bar assessed 1h before next meal, adapted from ref. 20
- Low fat yogurts are more satiating than fruit-based drinks:
Low fat yogurts, whether drinkable or eaten with a spoon, had a greater satiating effect (lower hunger and higher fullness ratings) than isocaloric fruit-based drinks or dairy fruit drinks (20).
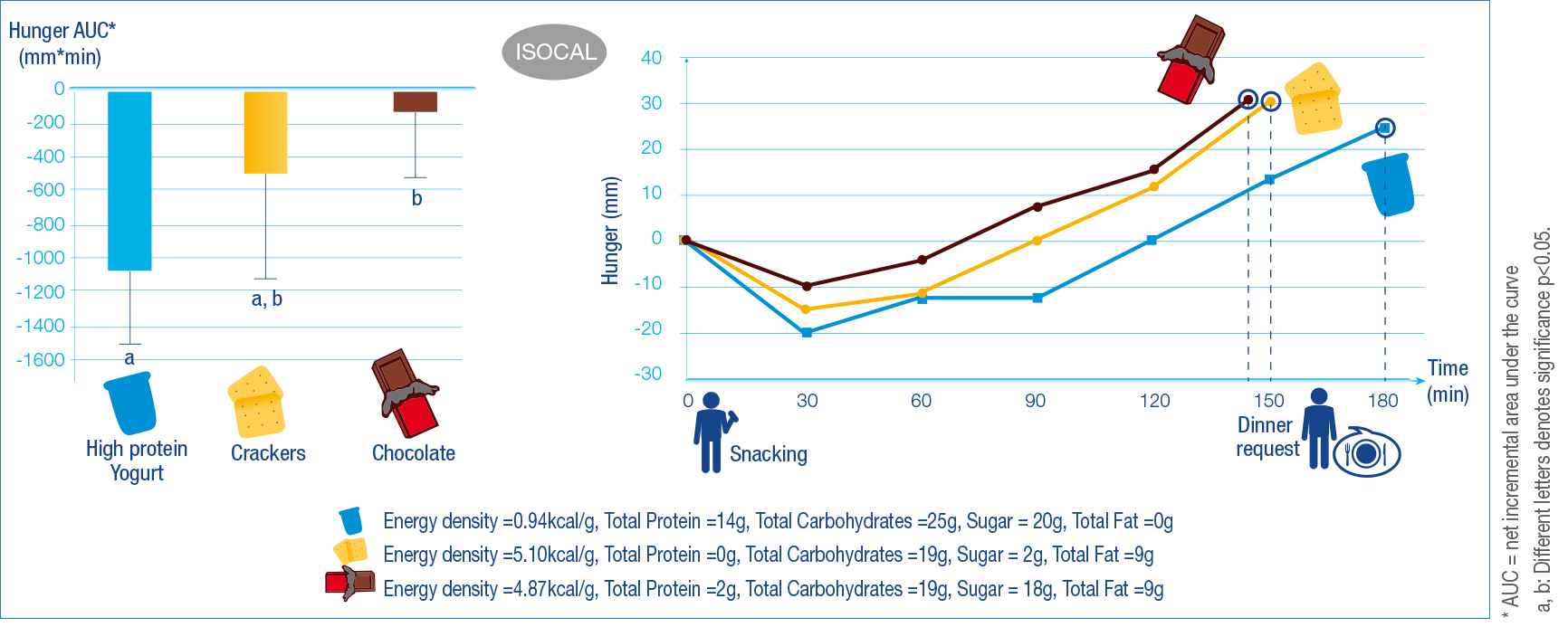
- High protein, less energy-dense snacks like yogurt can improve appetite control
When high protein less energy-dense snacks like yogurt are compared to high fat snacks having the same calorie content, consumption of the yogurt led to greater reduction in afternnoon hunger (p < 0.01). This study suggests that eating less energy dense, high-protein snacks like yogurt in place of isocaloric high fat snacks, can improve the control of appetite and energy intake in healthy women (21).