This Digest is all about #Snack, #Yogurt and #Satisfaction.
Nutrient composition and satiety
What you choose to snack on will depend on a host of factors, including availability of food, time, tempting aromas, and so on, and although a given snack may hit the spot at the time, not all snacks can be considered to be satisfying: a food that fills you up and keeps you going till your next meal.
Useful definitions
- Satiation is a set of complex processes that inhibits the motivation to eat during one eating event. Put more simply, it is a feeling of satisfaction that promotes the end of a meal.
- Satiety is presented as the inhibitory mechanism that takes place after the end of one eating episode and prevents the return of hunger for a variable duration in the post-prandial state. So, this is the stage when you stop eating when feeling full.
- Hunger: conscious sensation reflecting a mental urge to eat, which can be traced to changes in physical sensations in parts of the body – stomach, limbs or head. In its strong from, it may include feelings of light-headedness, weakness or emptiness in the stomach (3). So, this can be described as the physical sensation, felt mainly in the stomach, that triggers a need to eat.
Reference:
1. Blundell J, de Graaf C, Hulshof T et al. (2010) Appetite control: methodological aspects of the evaluation of foods. Obesity Reviews 11: 251–70.
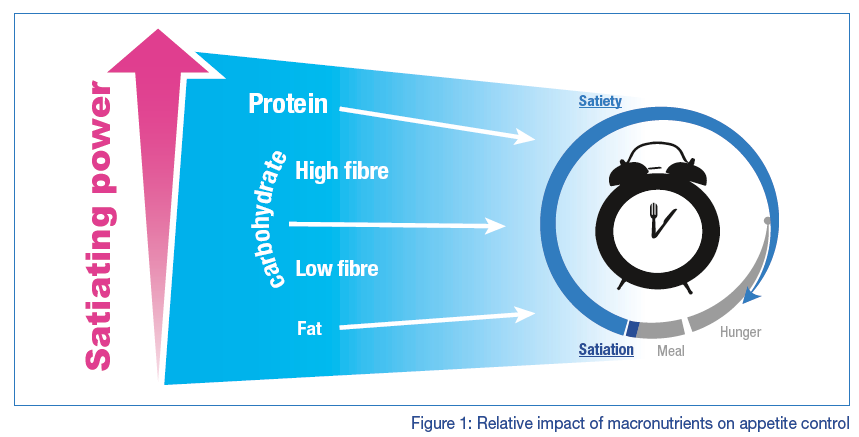
Impact on satiety of macronutrients
What makes a snack satisfying?
Different nutrients will have different effects on hunger and subsequent energy intake. That is why we don’t only snack when we’re hungry, but it is helpful to consider the impact that macronutrients within a snack may have on satiety if we are to enjoy a snacking experience that is less likely to show on our waistline.
Protein Power
There is strong evidence that proteins possess the highest satiating value of all the macronutrients (2, 3, 4). A review conducted in 2004 showed that higher protein intake was associated with a feeling of satiety hours after the high protein food was ingested (2). Several studies have shown that protein is more satiating than other macronutrients, possibly due to increased post-prandial thermic effects, altered gastrointestinal functions and postprandial metabolism, such as increased amino acid concentration and gluconeogenesis (5).
The Fibre Factor
Dietary fibres consist of naturally occurring plant materials that the body cannot digest. High fibre foods typically take longer to chew, and they are usually more bulky, helping to increase the volume of stomach contents. Additionally, fibre rich foods are passed more slowly through the digestive system, thereby increasing the length of time nutrients can interact with intrinsic signalling factors, which promote satiety and satiation (6).
Carbohydrate – quality counts
The concept of glycaemic index (GI) has been extensively studied and lower GI foods have been shown to have a beneficial effect of slowing down the rise in blood glucose after meals. Low GI foods are slowly digestible carbohydrates that are thought to be more satiating than high GI foods, and some studies have demonstrated a reduction in energy intakes and suppression of hunger cues after eating low GI meals (7). Many low GI foods are inherently high in fibre: beans, pulses, fruit, vegetables and oats, for example.
Fat Facts
Although gastric emptying is thought to be slower when we eat fat (4), preload studies suggest that fat has the least satiating power compared to the other macronutrients (8). Lawton (9) concluded that the most important aspect influencing the size of the meal at dinner was the nutrient content, rather than the level of hunger. When subjects were most hungry, they tended to overeat on high fat foods.
In conclusion, it appears that protein confers the highest satiating effect of all macronutrients. There is some research to indicate that protein from dairy foods has a more favourable effect on satiety.
References:
2. Halton TL, Hu FB (2004). The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety and weight loss: a critical review. J Am Coll Nutr 23(5):373-385.
3. Bellisle, F. (1-3-2008). Functional foods and the satiety cascade. Nutrition bulletin 33(1):8-14.
4. Mattes RD (2007). The role of macronutrients in appetite regulation. Canadian Journal of Dietetic Practice and Research 68(2).
5. Juvonen KR, Karhunen L, Vuori E et al (2011). Structure modi_cation of a milk protein-based model food affects postprandial intestinal peptide release and fullness in healthy young men. Br J Nutr. 2011; 106(12): 1890-8.
6. Slavin J, Green H (2007). Dietary _bre and satiety. Nutrition bulletin. Volume 32, Issue Supplement s1, 32–42.
7. Brand-Miller JC, Holt SH et al. (2002). Glycemic index and obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 76(1):281S-285S.
8. Skidmore P (2007). Macronutrient intakes and their role in obesity. Nutrition bulletin 32(s1):4-13.
Energy density and satiety
Energy density is a measure of the kcal/g in a given weight of food or drink. When we have free access to a range of foods, studies suggest that we will eat roughly the same volume of food each day. Rolls (10) showed that energy density of food impacted on calories consumed by both lean and obese women. They took in fewer calories when they ate low energy dense foods and they ate a similar volume, but not weight, of food.
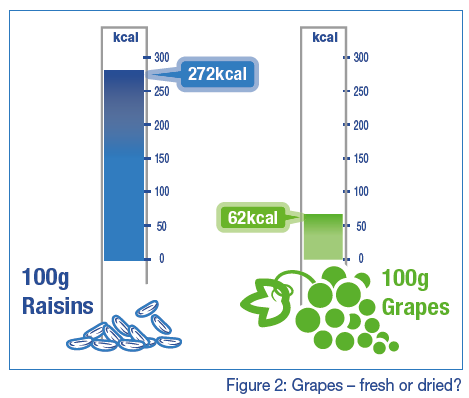
100g of grapes will have fewer calories than 100g of raisins, regardless of the fact that they are the same weight; if we choose foods that are lower in energy density, are we more likely to have a lower calorie intake? Energy density is important in the satiety response and may be more important than macronutrient content. Lower-energy density foods appear to be more satiating than higher-energy density foods. Compare how much fuller you would feel if you ate 100kcal of grapes compared to 100kcal of raisins (10).
Also energy density is influenced by fat intake, it can also be modified just by adding water, with the consequence that satiety might be increased without changing fat (11, 12).
References:
10. McCance and Widdowson’s the Composition of Foods: Seventh Summary Edition (2015). Public Health England.
11. Bell E and Rolls B, (2001). Energy density of foods affects energy intake across multiple levels of fat content in lean and obese women. AJCN 73: 1010-1018.
12. Bell EA, Castellanos, VH, Pelkman CL, et al (1998). Energy density of foods affects energy intake in normal-weight women. Am J Clin Nutr 67:412–20.
Physical & chemical characteristics of food & satiety: solid or liquid?
Sensory attributes of foods and beverages play an important role in eating behavior. For example, the physical form of a food can alter the sensation of fullness and satiety. Overall, study results consistently demonstrate that texture and viscosity affect different aspects of feeding behaviour, for example, ratings of hunger and fullness.
Solid or liquid?
The food texture experienced at the start of a meal or eating occasion may predict the duration of the sensory exposure to the food and, therefore, its expected satiating capacity. Think for a minute about your perception of how full you’re going to feel if you lower your spoon into a deliciously thick and creamy pot of yogurt with fruit chunks, compared to a thinner or lighter yogurt. Hogenkamp et al (13) put this to the test. In a study with yogurts and custards of different thickness and flavours, subjects consistently expected the thicker dairy foods to be more satiating. Flavour or means of consumption (via a straw or spoon) had no influence on expected satiation. Women tend to be lured into quick and easy solutions to weight management…now here’s an angle on how texture appears to affect women in particular: McCrickerd et al (14) found that increasing the perceived thickness of a drink (via increased viscosity) resulted in less consumption of the drink in female participants only. Does this suggest that women will select smaller portions when sensory characteristics such as thickness or flavour make them believe it will be more satiating? Could this have implications for regulating consumption and hence body weight?
The texture and food structure as well as the type of milk protein in a food can affect gastric emptying, digestion and absorption of nutrients, gastrointestinal hormone release, and appetite. A firmer food structure has been shown to enhance satiety and attenuate postprandial metabolic responses of foods containing different dairy foods (15).
In general, semi-solid and solid foods appear to be more satiating than liquid foods. Despite these consistent findings, there is a lack of data on whether the increased satiety observed when more viscous and thicker foods are consumed leads to differences in food intake over time. Research currently available suggests that subsequent food intake is not affected.
References:
13. Hogenkamp PS, Sta_eu A, Mars M, et al (2011). Texture, not _avor, determines expected satiation of dairy products. Appetite. 57(3): 635-41.
14. McCrickerd K, Chambers L, Yeomans MR (2014). Does modifying the thick texture and creamy flavour of a drink change portion size selection and intake? Appetite. 73:114-20.
15. Juvonen KR, Karhunen LJ, Vuori E, et al (2011). Structure modification of a milk protein-based model food affects postprandial intestinal peptide release and fullness in healthy young men. Br J Nutr; 106(12): 1890-8.
Physical & chemical characteristics of food & satiety: Thick or thin?
Sensory attributes of foods and beverages play an important role in eating behaviour. For example, the physical form of a food can alter the sensation of fullness and satiety. Overall, study results consistently demonstrate that texture and viscosity affect different aspects of feeding behaviour, for example, ratings of hunger and fullness.
Thick or thin?
Meal viscosity is an important determinant of satiety. Maricani et al (16) investigated the interaction between meal viscosity and nutrient content on the gastric emptying and satiety in humans. The results of this study showed that viscosity and calorie content have an additive effect on delaying gastric emptying and increasing the sense of satiety during meal consumption. High meal viscosity had a greater effect on the sense of satiety.
A crossover study by Mattes (17) examined the effects of viscosity on appetite in a comparison of thick and thin shakes. Hunger ratings were significantly lower following the ingestion of the more viscous shake and remained lower than baseline for a longer period of time. Postprandial satiety scores were higher after ingestion of more viscous foods as compared to liquid foods.
References:
16. Marciani L, Gowland PA, Spiller RC, et al (2001). Effect of meal viscosity and nutrients on satiety, intragastric dilution, and emptying assessed by MRI. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 280(6):G1227-33.
17. Mattes RD and Rothacker D (2001). Beverage viscosity is inversely related to postprandial hunger in humans. Physiol Behav. 74(4-5):551-7.
Physical & chemical characteristics of food & satiety: How much?
Sensory attributes of foods and beverages play an important role in eating behaviour. For example, the volume of foods can affect different aspects of feeding behavior. Overall, study results consistently demonstrate that texture, viscosity and volume affect different aspects of feeding behaviour, for example, ratings of hunger and fullness.
How much?
Water or even air incorporated into food has been shown to decrease energy intake. A study carried out by Rolls (18), in which the volume of milk-shakes was altered by incorporating air, has demonstrated the effect of volume alone, and confirmed that a significant increase in volume (> 150 ml) did transiently reduce the subjective appetite, and the food intake at a meal served 30 minutes later.
Increasing the volume of a food by diluting the food increases its weight and reduces its energy density. Davy (19) showed that a water preload decreased intake at a breakfast test meal. Addition of water to increase volume of food, or giving water or soup as a “preload” before a meal, increases immediate feelings of satiety and decreases subsequent food intake, even if the effects of simple additions are generally very short-lasting (20, 21, 22).
References:
- Rolls BJ, Bell EA et al. (1999). Water incorporated into a food but not served with a food decreases energy intake in lean women. Am J Clin Nutr 70(4):448-455.
- Davy BM1, Dennis EA, Dengo AL et al (2008). Water consumption reduces energy intake at a breakfast meal in obese older adults. J Am Diet Assoc. Jul;108(7):1236-9.
- Kirkmeyer SV, Mattes RD (2000). Effects of food attributes on hunger and food intake. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(9):1167-1175.
- Himaya A, Louis-Sylvestre J (1998). The effect of soup on satiation. Appetite 30(2):199-210.
- Lappalainen R, Mennen L et al. (1993). Drinking water with a meal: a simple method of coping with feelings of hunger, satiety and desire to eat. Eur J Clin Nutr 47(11):815-819.
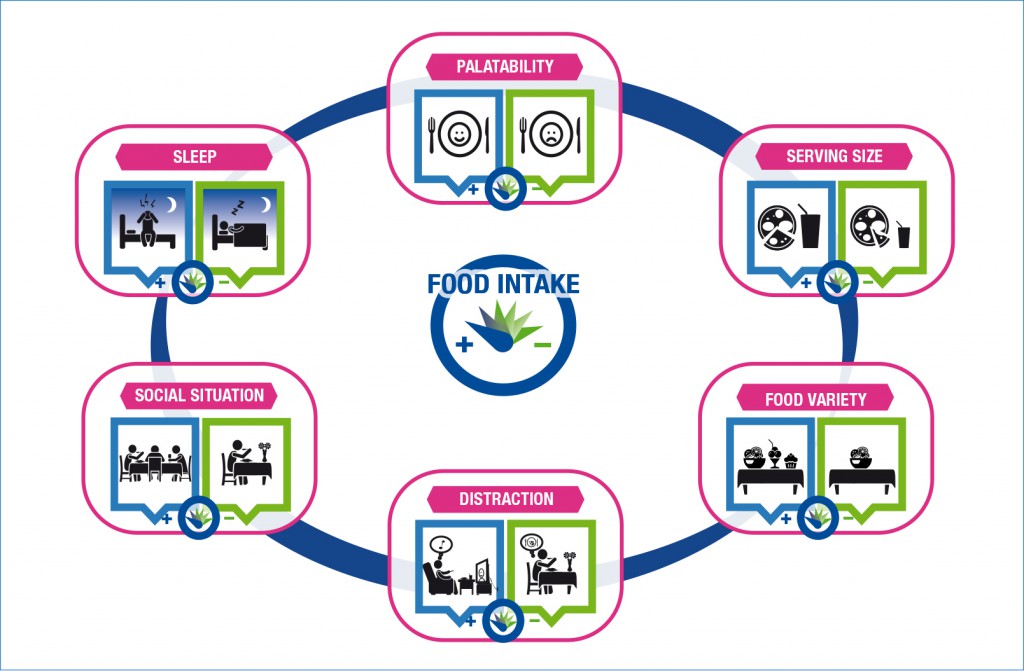
External Influences on Food Intake
Despite the well developed internal physiological mechanisms that work to regulate appetite (see Yogurt Nutrition Digest 2), in societies where we are fortunate enough to have a plentiful food supply, the reality is that satiety is easily influenced by a range of external factors including our immediate environment. The sight, smell, taste and availability of food can simply be too tempting, or comforting, regardless of how full we are feeling. In addition, some people may have weaker satiety signals or be less sensitive to these signals, putting them at additional risk of overeating, and in turn weight gain (23). Awareness of these influences and developing strategies to better manage them, including making food choices that help promote internal satiety, is all part of skill development for healthy weight management. A study by Drapeau et al (24) showed that baseline satiety quotient scores tended to be negatively correlated with external hunger, anxiety and eating at night. The low satiety phenotype showed a lower cortisol response to the test meal, so stress could be involved in the low satiety phenotype. Globally, these results may help understanding why some individuals report weak appetite sensations and thus, have higher susceptibility to overeating
References:
- O’Rahilly S & Farooqi IS (2008). Human obesity: a heritable neurobehavioral disorder that is highly sensitive to environmental conditions. Diabetes. 57 (11): 2905-10.
- Drapeau V et al (2013). Behavioural and metabolic characterisation of the low satiety phenotype. Appetite 70: 67-72.
Where does yogurt fit in?
Yogurt, and in particular protein-rich yogurt, is an example of a nutritious food that when eaten as a snack has been shown to increase satiety between meals (lower hunger and higher fullness ratings) in a number of studies (25, 26, 27).
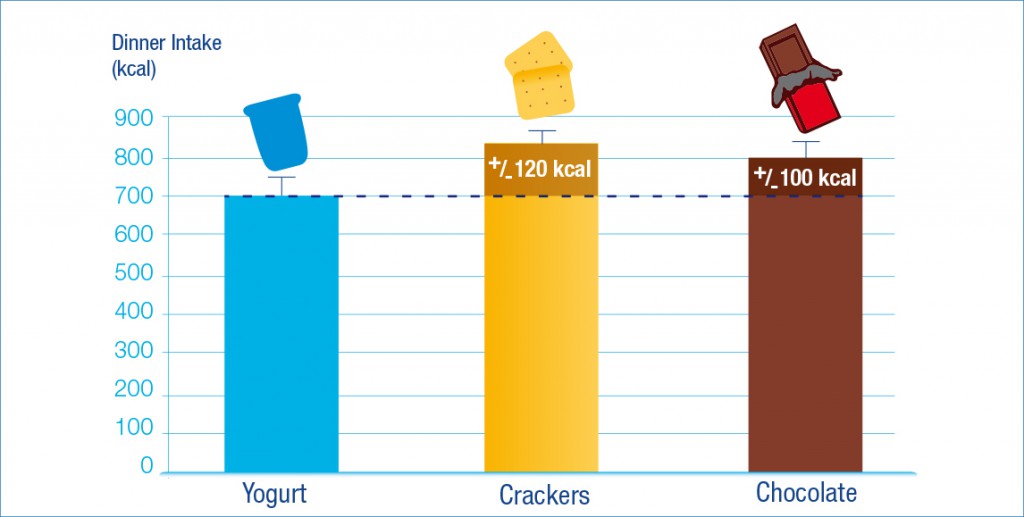
Recently, Ortinau et al (28) demonstrated that eating 160 kcal of a high protein yogurt snack reduced hunger to a greater extent than 160kcal of a high fat chocolate snack. The yogurt snack led to approximately 100 fewer kcals to be eaten at dinner when compared to the chocolate, and it also delayed eating by about 30 minutes. This study suggests that an afternoon snack that has a lower energy density and a higher protein content, such as yogurt, could be helpful in improving the control of appetite and calorie intake in healthy women. For more details on this study, see Yogurt Nutrition Digest 2.
The body of research suggests there is the potential for high protein snacks such as protein-enriched yogurt, to prevent further snacking and overeating during the subsequent hours. Consumption of low energy-dense foods also helps to reach satiety relatively quickly, further substantiating the role that protein-rich yogurt could play in hunger management.
References:
- Douglas SM, Ortinau, LC, Hoertel HA, et al. (2013). Low, moderate, or high protein yogurt snacks on appetite control and subsequent eating in healthy women. Appetite; 60, 117-122.
- Tsuchiya A, Almiron-Roig E, Lluch A et al. Higher satiety ratings following yogurt consumption relative to fruit drink or dairy fruit drink. J Am Diet Assoc. 2006;106 (4):550-7.
- Chapelot D, Payen F. Comparison of the effects of a liquid yogurt and chocolate bars on satiety: a multidimensional approach. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(5):760-7.
- Ortinau et al. Effects of high-protein vs. high- fat snacks on appetite control, satiety, and eating initiation in healthy women Nutrition Journal 2014, 13:97. http://www.nutritionj.com/content/13/1/97.