Vitamin A is an essential compound to health at every life stage. What are its functions and where to find it?
What is vitamin A?
Vitamin A is essential at every stage of life. It contributes to the mechanism of vision. Vitamin A is present in the light sensitive protein rhodopsin in the retina and helps the differentiation of the membrane and cornea in the eye.
It is also involved in the regulation (activation, repression) of gene expression, and is thus implicated in numerous bodily functions: embryonic development, cell growth, tissue renewal (skin, intestinal mucosa), immune system…
Deficiency can lead to night blindness and in most serious cases permanent blindness. During pregnancy and early childhood, it can cause abnormal lung development and risk of anaemia. However, vitamin A deficiency is quite rare in developed countries, as most people get enough vitamin A in their diet.
Dietary recommendations
In the diet, Vitamin A can be found in two main forms; retinol and carotenoids:
- Retinol is the form of vitamin A that is best absorbed and metabolised directly by the human body as it is pre-formed vitamin A.
- Carotenoids (such as beta-caroten) are precursors (pro-vitamin A), absorbed and converted into vitamin A.
Thus, diet recommendations are given in Retinol Equivalent (RE) and 1µg RE is 6µg of beta-carotene and 12µg of other carotenoids.
The recommendation is of 650-750 µg RE for healthy adults, 700µg RE during pregnancy and 1300µg RE during lactation.
It is recommended to consume no more than 3000 µg RE per day for adults including during pregnancy and lactation, as an excess in vitamin A can increase the risk of birth defects, and not more than 1500µg RE per day, in postmenopausal women, as it could increase bone fracture risk.
Dietary sources of Vitamin A
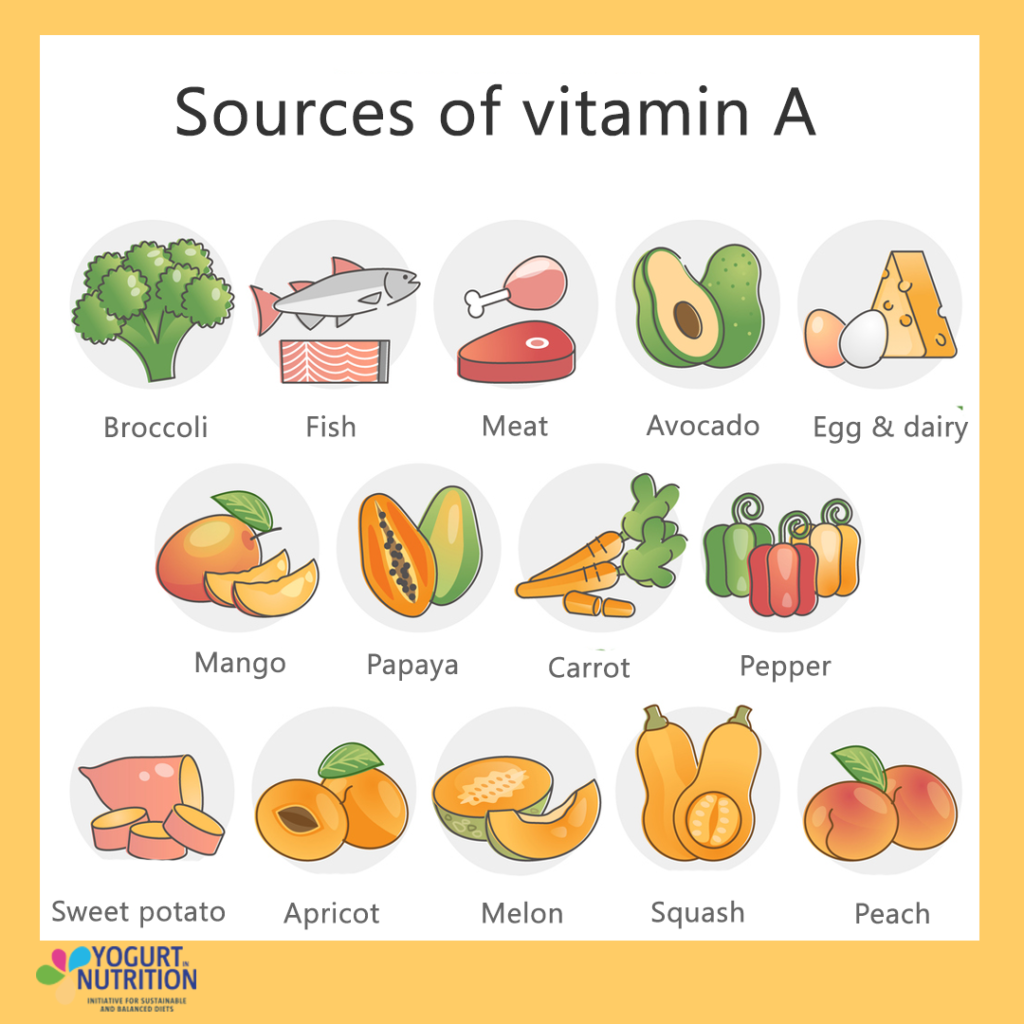
Vitamin A can be found in plant and animal sources.
In vegetables, vitamin A is found in the form of carotenoids. They are responsible for the orange and red pigments of plants and we find it in vegetable or fruits such as carrots, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, mango or melon. They are also present in dark leafy green vegetables (kale, spinach for example).
Animal sourced-food contain vitamin A in the form of retinol. It can be found for example in dairy, eggs, liver meats.
Vitamin A in dairy
In dairy, vitamin A is found mostly as retinol and a little bit of beta carotene.
Most dairy products are also a source of lipids which help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin A
Fat free dairy contains much less vitamin A.
That is why when choosing a yogurt, it is best to choose one with some fat (whole milk or semi skimmed milk dairy) to optimize vitamin A intakes.




