A cross-sectional survey examined the link between consumption of yogurt and adherence to dietary guidelines of 2.557 adults (18-59 years) in São Paulo. A questionnaire assessed the consumption frequency of fermented milk, whole and skimmed yogurt, as well as socioeconomic and demographic data. A Quantitative Food Frequency Questionnaire collected data on habitual intake of 65 food items, representative for the local population.
Yogurt stimulates a better adherence to dietary guidelines
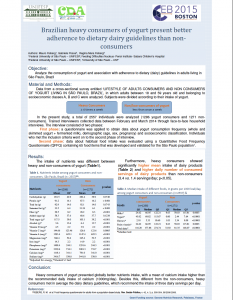 Heavy consumers ate more than 4 servings of yogurt per day and their mean calcium intake was higher than the Brazilian recommendations of 1000mg/day. The nutrient intake of proteins, fibers, vitamins (A,C and D), magnesium, phosphorus and potassium was higher, compared to non-consumers. Frequent yogurt consumers showed a higher mean intake of dairy products, such as milk and cheese, and showed a better compliance to dairy dietary guidelines of three servings per day.
Heavy consumers ate more than 4 servings of yogurt per day and their mean calcium intake was higher than the Brazilian recommendations of 1000mg/day. The nutrient intake of proteins, fibers, vitamins (A,C and D), magnesium, phosphorus and potassium was higher, compared to non-consumers. Frequent yogurt consumers showed a higher mean intake of dairy products, such as milk and cheese, and showed a better compliance to dairy dietary guidelines of three servings per day.



