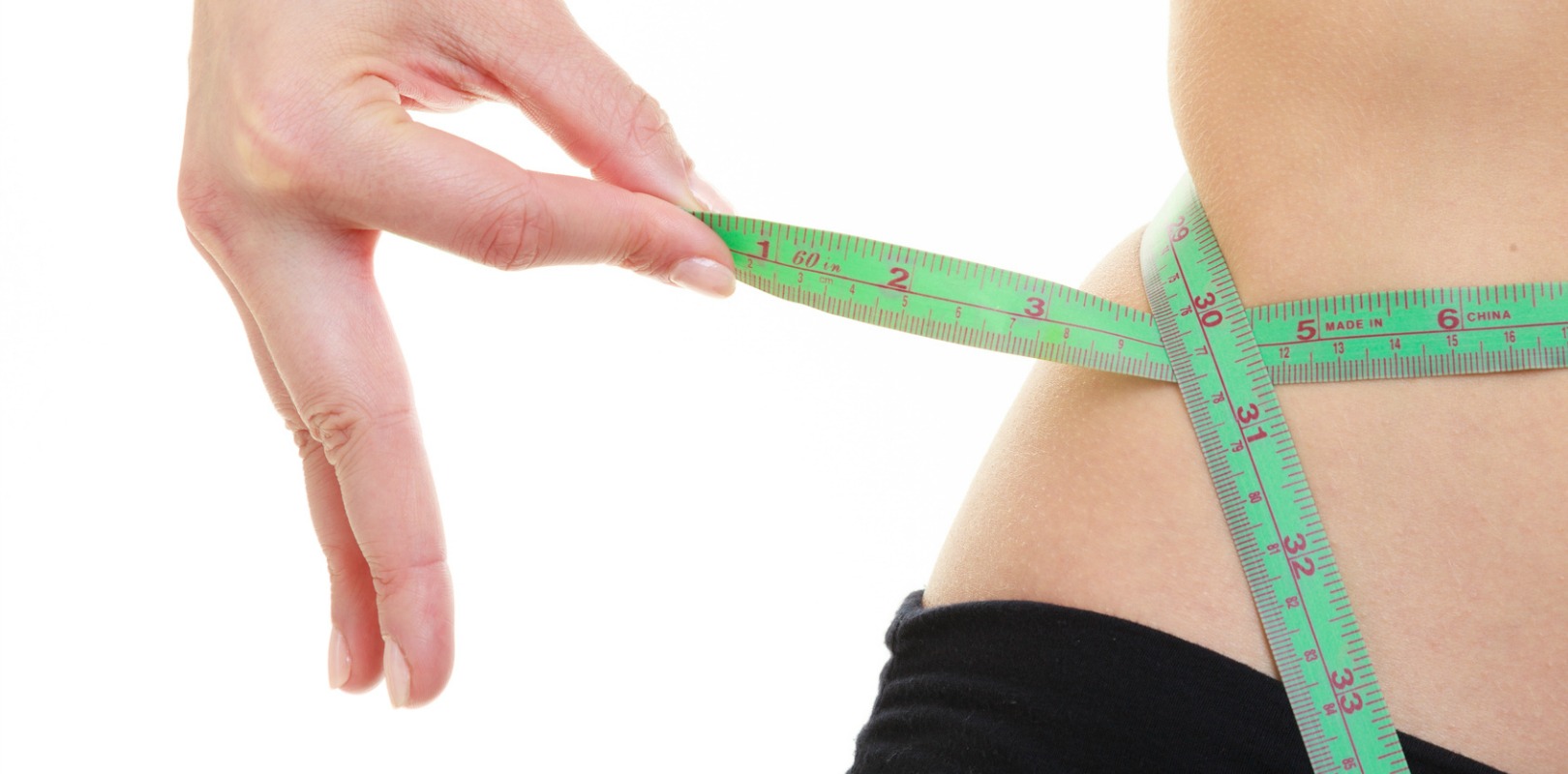
This study examined relationships between energy, protein and calcium consumption from dairy foods (milk, yoghurt, cheese, dairy spreads, ice-cream) and adiposity (BMI, waist and hip circumference (WC and HC, dual energy X-ray absorptiometry) in 720 overweight/obese Australian +50 men and women.
Reduced-fat milk was the most commonly consumed dairy product (235 g/day), followed by whole milk (63 g/day) and yoghurt (53 g/day). Overall dairy food consumption (g/day) was significantly and inversely associated with BMI, % of body fat and WC. Dairy protein and dairy calcium were both inversely associated with all adiposity measures.
Yogurt consumption was inversely associated with % body fat, abdominal fat, WC and HC, while reduced-fat milk consumption was inversely associated with BMI, WC, HC and % body fat.