The lifestyle of 2.610 adults (18-59 years) in São Paulo was examined using a cross-sectional survey. Half of the participants were regular yogurt consumers with more than 4 servings a week, the other half consumed yogurt less than once a week. The household interviews took place in two phases: firstly, they collected data on consumption frequency of whole and skimmed yogurt and fermented milk, on demographic and socioeconomic status. Secondly, lifestyle characteristics, habitual food intake and presence of morbidity were surveyed.
Yogurt is associated with a healthier lifestyle
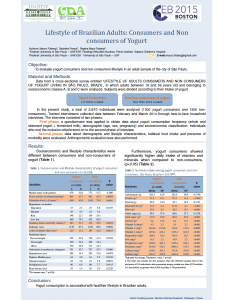 Socioeconomic and lifestyle discrepancies were found between both groups: yogurt consumers had a higher education level, less dependence of alcohol and more physical activity, while non-consumers had a higher smoking status, were more overweight and showed a higher risk for diabetes, hypertension and heart disease. Yogurt consumers had also a significantly higher daily intake of vitamins and minerals compared to non-consumers and were associated with a healthier lifestyle.
Socioeconomic and lifestyle discrepancies were found between both groups: yogurt consumers had a higher education level, less dependence of alcohol and more physical activity, while non-consumers had a higher smoking status, were more overweight and showed a higher risk for diabetes, hypertension and heart disease. Yogurt consumers had also a significantly higher daily intake of vitamins and minerals compared to non-consumers and were associated with a healthier lifestyle.



