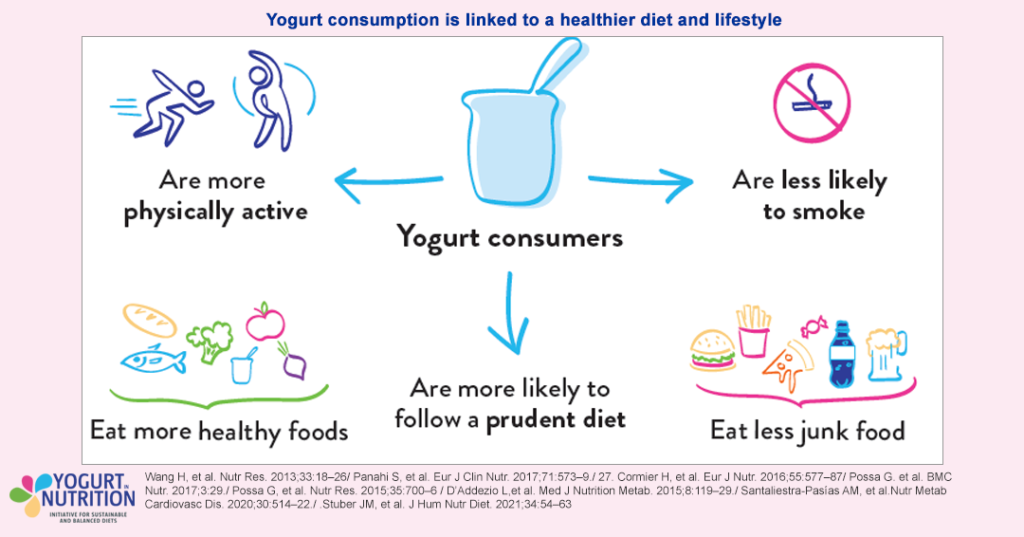
Regular yogurt consumers of all ages tend to eat and live healthily. They are less likely to eat unhealthy foods, or smoke or drink alcohol to excess, and are more likely to exercise regularly than people who don’t.
Regular yogurt consumers tend to choose healthy diets
Yogurt consumption is associated with better diet quality, measured using validated indices of healthy eating, among both children and adults in the USA, Canada and Europe.
Regular yogurt consumers are less likely to consume unhealthy food and more likely to stick to dietary guidelines than non-consumers.
In adults
Compared with those who eat little or no yogurt, people who eat yogurt frequently have a better diet quality and tend to follow dietary guidelines more closely.
Yogurt consumers score more highly on the Healthy Eating Index (HEI) than non-consumers, which could be partly explained by a significant increase in fruit, grain and dairy consumption.
Yogurt consumers are more likely to have a diet with more fruits, vegetables, nuts, legumes, fish and seafood, and fewer fast foods such as French fries and fried foods, processed and red meats, pizza, snacks, soft drinks and alcohol.
People who frequently consume yogurt have higher nutrient intakes than those who do not often eat yogurt even when yogurt is not a source of these nutrients. Hence frequent yogurt consumers (at least one serving per day) have been found to have higher intakes of folic acid, copper, manganese and iron.
Both in children and in adults (in Spain and the USA), swapping high-calorie, nutrient-poor snacks for full fat yogurt with fruit could help boost key nutrients and improve dietary quality without contributing to dietary excess and obesity.
In children
Young children who regularly consume yogurt have a better diet quality and the overall nutrient content of their diets is higher than those who don’t.
The diets of children who eat yogurt regularly are better overall than non-consumers – they consume more fruit, whole grains and total dairy and fewer fatty foods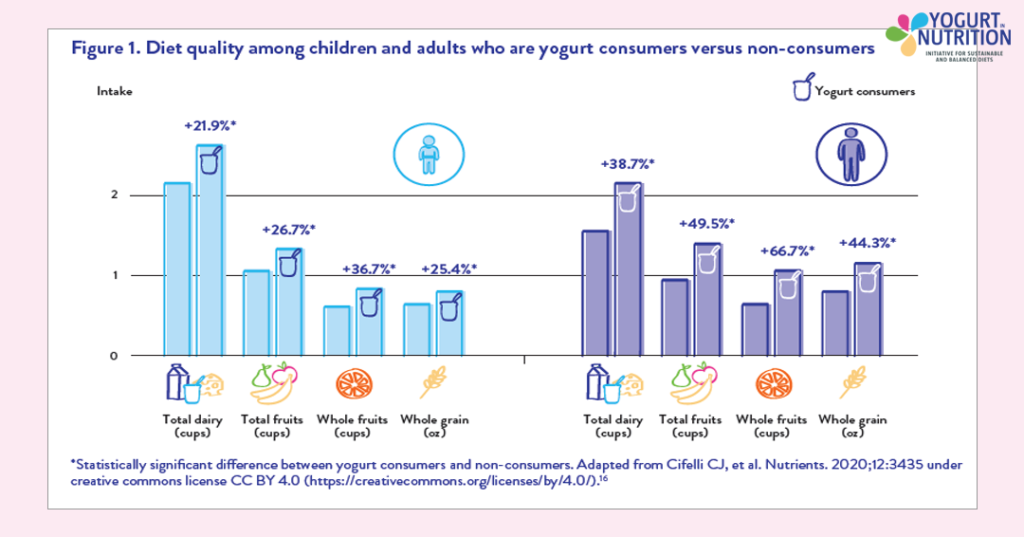
Yogurt consumption is a marker of a healthier lifestyle
Numerous studies suggest yogurt consumption is also a signature of a healthy lifestyle. Compared with people who do not eat yogurt, those who do consume yogurt:
- are generally healthier and leaner. They also tend to be more highly educated and of higher socioeconomic status.
- show healthier non-nutritional behaviour: they are less likely to smoke, tend to drink less alcohol and are more likely to be physically active in their leisure time than non-consumers.
- tend to have a better health-related quality of life and mental health.
Children who regularly consume milk and yogurt are more likely than those who don’t to engage in healthy lifestyle behaviours with more physical activity and less sitting in front of a screen.
“Yogurt consumption is a signature of healthy living. Compared with non-consumers, people who regularly eat yogurt tend to have better diet quality, have a more active lifestyle, drink less alcohol, and are less likely to smoke. “
Sources:
- Zhu Y, Jain N, Holschuh N, et al. Associations between frequency of yogurt consumption and nutrient intake and diet quality in the United Kingdom. J Nutr Sci. 2021;10:e85.
- Williams EB, Hooper B, Spiro A, et al. The contribution of yogurt to nutrient intakes across the life course. Nutr Bull. 2015;40:9–32.
- Keast DR, Hill Gallant KM, Albertson AM, et al. Associations between yogurt, dairy, calcium, and vitamin D intake and obesity among U.S. children aged 8–18 years: NHANES, 2005–2008. Nutrients. 2015;7:1577–93.
- Cifelli CJ, Agarwal S, Fulgoni VL. Association of yogurt consumption with nutrient intakes, nutrient adequacy, and diet quality in American children and adults. Nutrients. 2020;12:3435.
- Vatanparast H, Islam N, Prakash Patil R, et al. Consumption of yogurt in Canada and its contribution to nutrient intake and diet quality among Canadians. Nutrients. 2019;11:1203.
- Wang H, Livingston KA, Fox CS, et al. Yogurt consumption is associated with better diet quality and metabolic profile in American men and women. Nutr Res. 2013;33:18–26.
- Panahi S, Fernandez MA, Marette A, et al. Yogurt, diet quality and lifestyle factors. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2017;71:573–9.
- Cormier H, Thifault É, Garneau V, et al. Association between yogurt consumption, dietary patterns, and cardio-metabolic risk factors. Eur J Nutr. 2016;55:577–87.
- D’Addezio L, Mistura L, Sette S, et al. Sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics of yogurt consumers in Italy: results from the INRAN-SCAI 2005–06 survey. Med J Nutrition Metab. 2015;8:119–29.
- Mena-Sánchez G, Babio N, Martínez-González MA, et al. Fermented dairy products, diet quality, and cardiometabolic profile of a Mediterranean cohort at high cardiovascular risk. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;28:1002–11.
- Santaliestra-Pasías AM, González-Gil EM, Pala V, et al. Predictive associations between lifestyle behaviours and dairy consumption: the IDEFICS study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;30:514–22.
- Iglesia I, Intemann T, De Miguel-Etayo P, et al. Dairy Consumption at Snack Meal Occasions and the Overall Quality of Diet during Childhood. Prospective and Cross-Sectional Analyses from the IDEFICS/I. Family Cohort. Nutrients. 2020;12:642.
- Stuber JM, Vissers LET, Verschuren WMM, et al. Substitution among milk and yogurt products and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes in the EPIC-NL cohort. J Hum Nutr Diet. 2021;34:54–63.
- Le Roy CI, Alexander Kurilshikov A, Leeming ER, et al. Yoghurt consumption is associated with changes in the composition of the human gut microbiome and metabolome. BMC Microbiology. 2022;22:39.
- Fernandez MA, Marette A. Potential health benefits of combining yogurt and fruits based on their probiotic and prebiotic properties. Adv Nutr. 2017;8:155S–64S.
- Hess J, Slavin J. Snacking for a cause: nutritional insufficiencies and excesses of U.S. children, a critical review of food consumption patterns and macronutrient and micronutrient intake of U.S. children. Nutrients. 2014;6:4750–9.
- Wajszczyk B, Charzewska J, Chwojnowska Z, et al. [Yogurt consumption and nutritional quality of daily diets in four years old children.] Żywienie Człowieka i Metabolizm [Human Nutrition and Metabolism]. 2013;40:166–80.
- Rivera-Dommarco J, López-Olmedo N, Aburto-Soto T, et al. Consumo de productos lácteos en población mexicana. Resultados de la Encuesta Nacional de Salud y Nutrición 2012. México: Instituto Nacional de Salud Pública, 2014.
- Zhu Y, Wang H, Hollis JH, et al. The associations between yogurt consumption, diet quality, and metabolic profiles in children in the USA. Eur J Nutr. 2015;54:543–50.
- Lecerf J-M, Colin J, Hebel P, et al. Les consommateurs de produits laitiers frais : des consommateurs comme les autres? Analyse de leurs profils alimentaires et nutritionnels (Who are fresh dairy products consumers? Analysis of their dietary and nutritional profiles). Nutrition Clinique et Métabolisme. 2016;30:11–21.
- Tremblay A, Panahi S. Yogurt consumption as a signature of a healthy diet and lifestyle. J Nutr. 2017;147:1476S–80S.
- Gopinath B, Flood VM, Burlutsky G, et al. Dairy food consumption and health-related quality of life in boys: preliminary findings from a 5-year cohort study. J Am Coll Nutr. 2016;35:522–8.